
Call to Negro America to March on Washington for Jobs and Equal Participation in National Defense, 1941
Primary Document by A. Philip Randolph
In 1941, A. Philip Randolph, the president of the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters, issued a call to African Americans to fight the unjust conditions in the workforce with a March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. The threatened mass protest forced President Franklin Roosevelt to sign Executive Order 8802 in June 1941, banning discrimination in the federal government and the defense industry. On June 28, A. Philip Randolph postponed the march.

1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom Statement and Demands
By heads of ten organizations calling for the March of August 28, 1963
The 1963 March on Washington had a list of ten demands. Half of the demands were not about integration or education – they were about labor and economic rights.
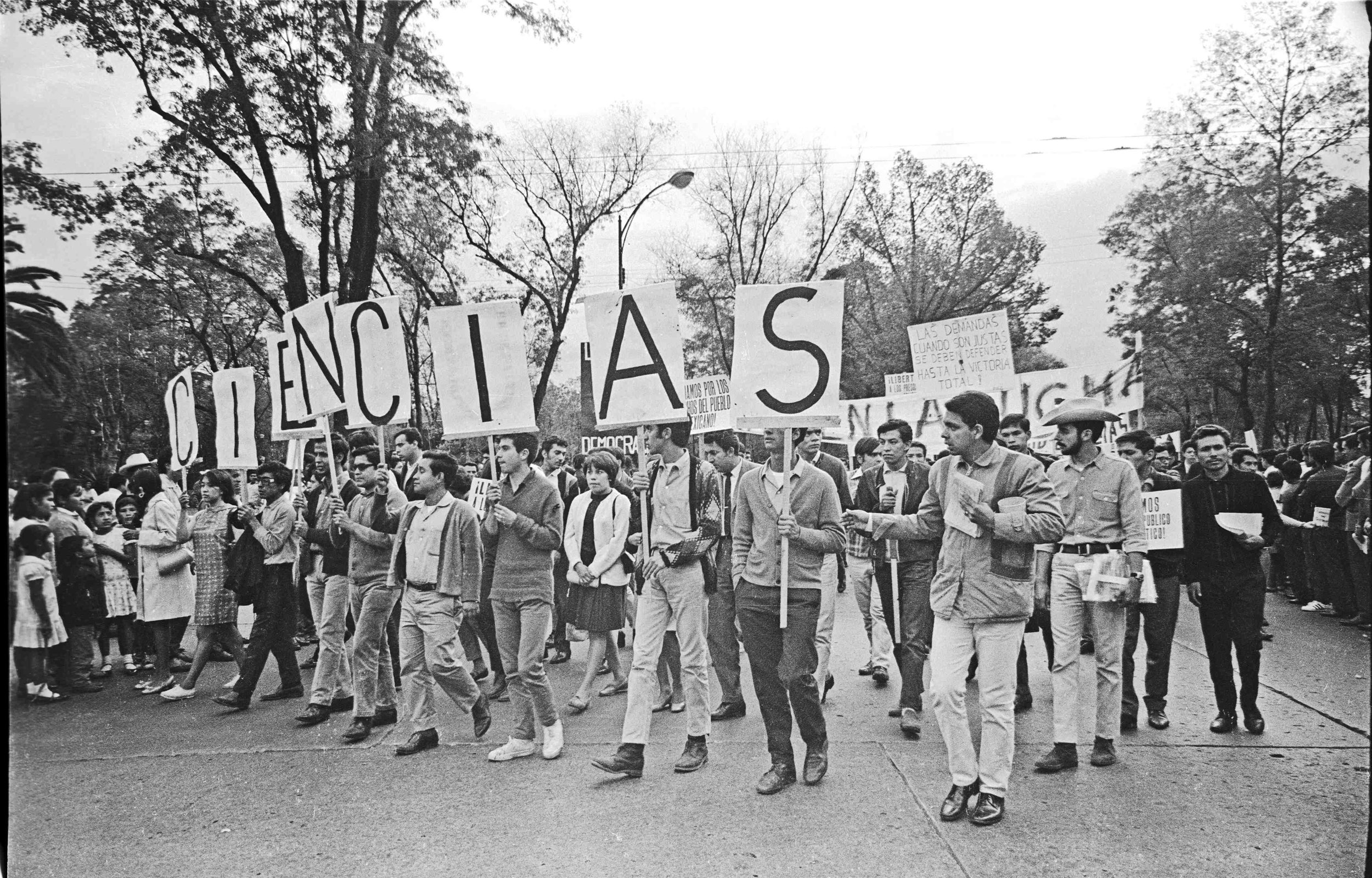
SNCC Memorandum of Solidarity with the Students of Mexico, October 1968
Primary Document by Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee In 1968, students organized to protest the lack of true democracy in Mexico. The tension began in July, but the climax came on October 2, 1968 — 10 days before the Olympic games were to begin in Mexico City. On this date, the police and army fired on thousands of demonstrators. Hundreds were killed, thousands were beaten and jailed, and the government did its best to sweep the incident under the rug.

McComb Statement Against the Vietnam War, July 1965
Reading by SNCC Digital Gateway.
In July 1965, a group of young activists in McComb, Mississippi’s Movement learned that John Shaw, one of their former classmates at Burglund High School, was killed in combat in Vietnam. Their statement written in response about the reasons why African Americans should not serve in Vietnam was the first anti-war statement from within the Civil Rights Movement. It paved the way for SNCC to take a stance against the war.

Vietnam: An Anti-War Comic Book
Primary Document by Julian Bond
A history of the Vietnam War and examples of African American opposition to the war, presented in an easy to read comic book format.

Nonviolence vs. Jim Crow
Primary Document by Bayard Rustin
This essay, based on an experience Rustin had in 1942, is one example of the countless challenges to Jim Crow and the use of non-violence as a tactic that predate the traditional 1954 start date for the Civil Rights Movement.

My Students Convinced Me to Let Go of Old School Teaching
Teaching Reflection by Susan Nail
A teacher reflects on incorporating primary documents and group work into her teaching.
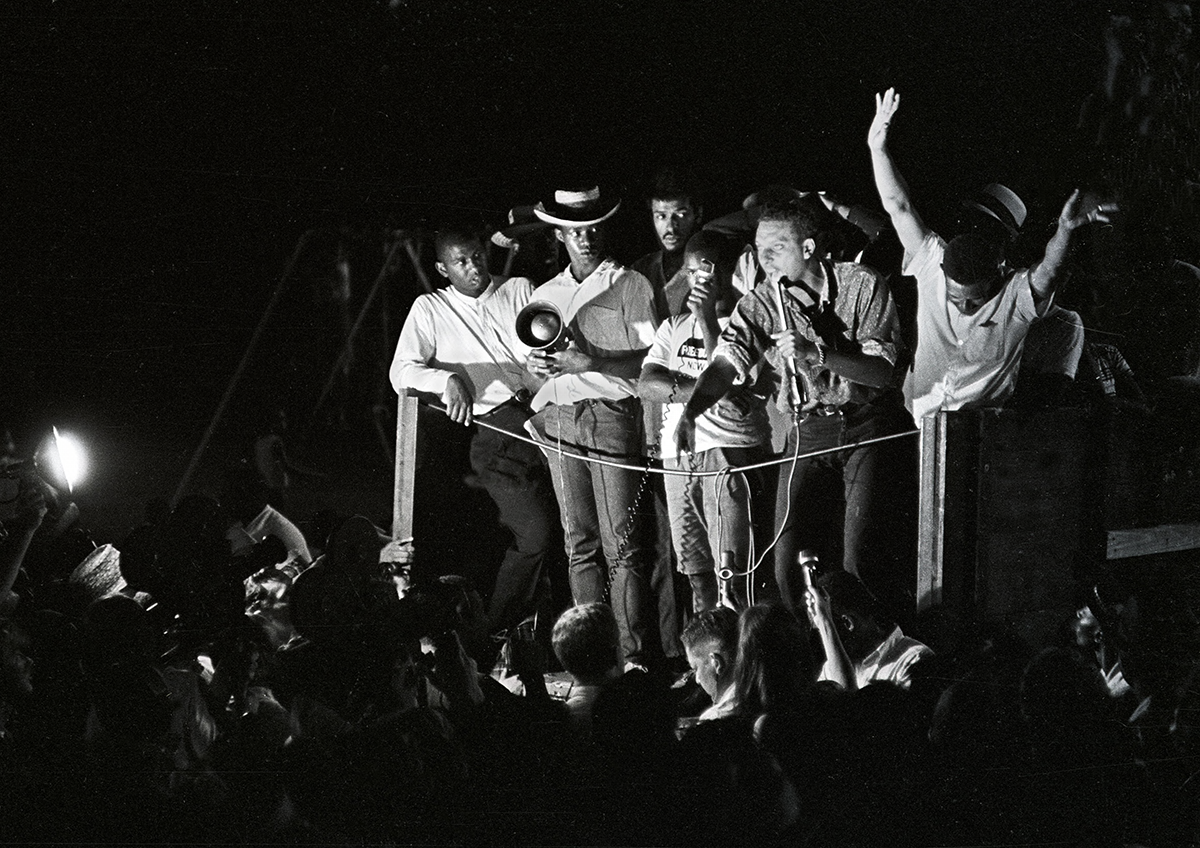

What We Want
Primary Document By Kwame Ture (Stokely Carmichael)
Separatism−the determination of a particular group of people to resist assimilating to the majority culture−has a long history in the United States. This excerpt from the “What We Want” speech offers a rationale for the notion of an independent Black community.
