
March on Washington Hidden History Quiz
Quiz by Teaching for Change
When most people think of the 1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, what comes to mind is Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s iconic statement, “I Have a Dream.” In truth, there was much more to this historic event than these four words in King’s speech. Teaching for Change designed this quiz about the 1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom to challenge assumptions, deepen understanding, and inspire further learning.
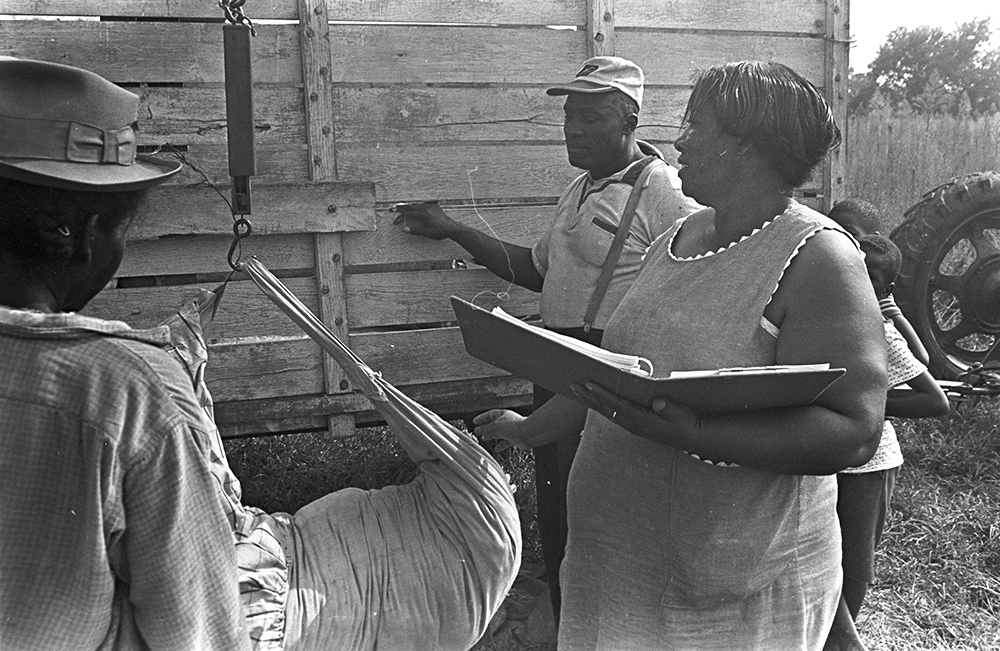

Introduction: Labor and Land
Labor and land have always been central to the struggle for civil and human rights in the United States. In this introduction, we share a few examples.

Call to Negro America to March on Washington for Jobs and Equal Participation in National Defense, 1941
Primary Document by A. Philip Randolph
In 1941, A. Philip Randolph, the president of the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters, issued a call to African Americans to fight the unjust conditions in the workforce with a March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. The threatened mass protest forced President Franklin Roosevelt to sign Executive Order 8802 in June 1941, banning discrimination in the federal government and the defense industry. On June 28, A. Philip Randolph postponed the march.
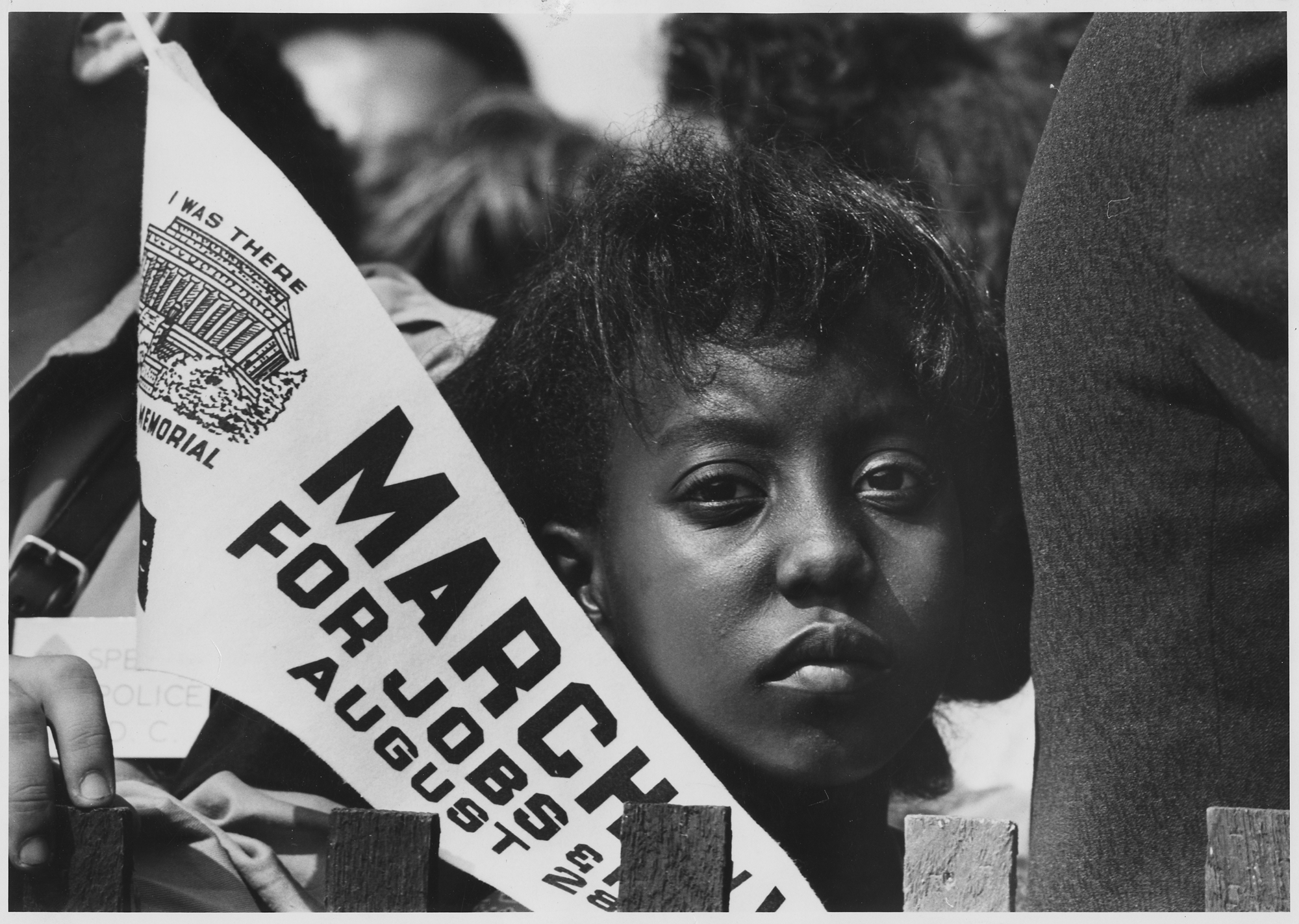
Claiming and Teaching the 1963 March on Washington
Reading by Bill Fletcher Jr.
The March on Washington did not begin as a classic civil rights march. It is barely remembered that the March on Washington was for freedom AND jobs, or that the march was initiated by black labor leaders.

At the River I Stand: The 1968 Memphis Sanitation Workers Strike and the Assassination of Martin Luther King Jr.
Reading by California Newsreel
The documentary film At the River I Stand skillfully reconstructs the two eventful months that transformed a strike by Memphis sanitation workers into a national conflagration, and disentangles the complex historical forces that came together with the inevitability of tragedy at the death of Martin Luther King Jr.
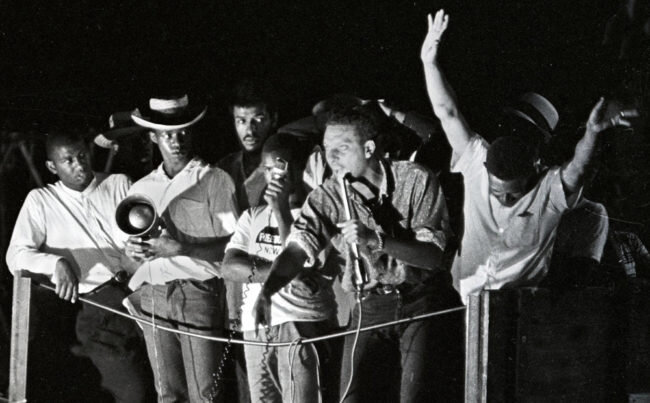

What Happened to the Civil Rights Movement After 1965? Don’t Ask Your Textbook
Reading by Adam Sanchez
Too often, students are taught that the Civil Rights Movement ended in 1965 with passage of the Voting Rights Act. It didn’t. Adam Sanchez argues that it is essential to teach the long, grassroots history of the Civil Rights Movement in order to help students think about today’s movements for racial justice.

The Unknown Origins of the March on Washington: Civil Rights Politics and the Black Working Class
Reading by William P. Jones
“The very decade which has witnessed the decline of legal Jim Crow has also seen the rise of de facto segregation in our most fundamental socioeconomic institutions,” veteran civil rights activist Bayard Rustin wrote in 1965. The March on Washington addressed the economic crisis facing working-class African Americans more effectively than any other mobilization since the Second World War.

Remembering the Memphis Sanitation Workers’ Strike: A Collaborative Mural
Lesson by Patty Bode and Stephanie Schmidt
An art lesson designed to introduce the complexity and role of ordinary people in the Civil Rights Movement. The addendum provides a practical guide to drawing images of people for murals.
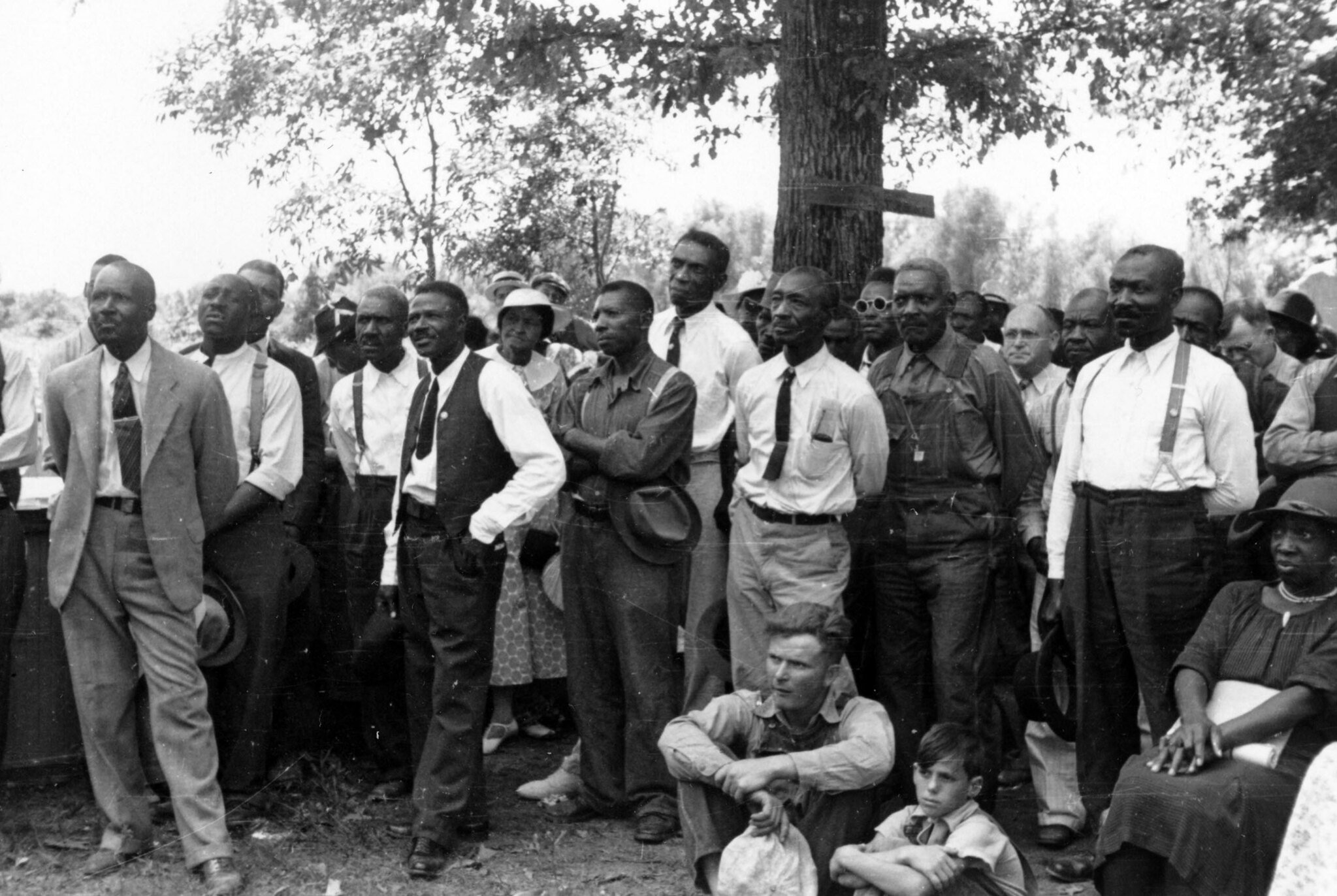

Southern Tenant Farmworkers: Black and White Unite?
Lesson By Bill Bigelow
This lesson examines efforts by Black and white workers to overcome the deep divisions and suspicions of racial antagonism in 1934 Arkansas. Students are faced with a “What would you do?” assignment that helps them understand many of the difficulties in achieving some degree of racial unity. At the same time, they realize the importance of confronting and overcoming racist attitudes.
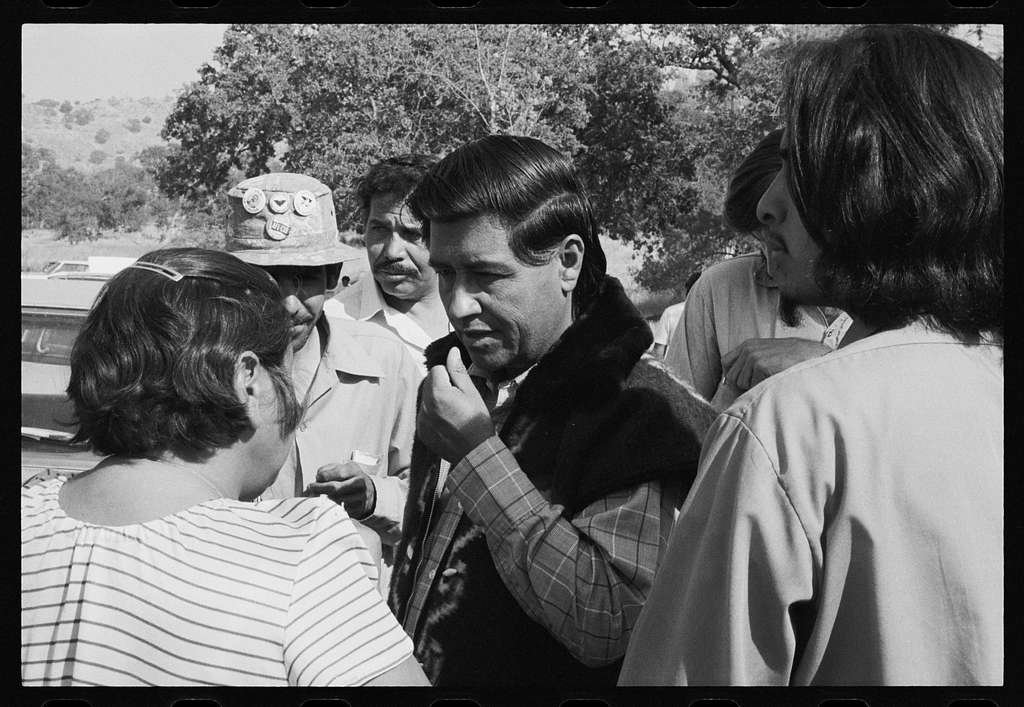

César Chávez on How It Began
Interview with César Chávez by Luis Torres
In an interview just before his death in 1993, César Chávez related the story of how the fledgling National Farm Worker Association (NFWA) union became involved with Filipino workers belonging to the Agricultural Workers Organizing Committee and the strike against major grape growers.

A Brief History of Black Cooperatives in the United States
Interview of Dr. Jessica Gordon Nembhard By Mira Luna
For as long as there have been Africans in America, there have been examples of Black social, cultural and economic solidarity. Often formed in response to systemic exclusion and economic stagnation, examples range from mutual aid networks, to freedom farms and grocery cooperatives.
